With the official release of GPT-5, many users are paradoxically trying to turn GPT-5 into the older GPT-4o. This seemingly “regressive” behavior actually reflects users’ complex needs for model performance, stability, and an emotional companion. While GPT-5 excels in numerous benchmarks, some of its characteristics in real-world applications don’t fully align with certain user scenarios. This article will explore the reasons behind this preference for the older model and provide a detailed tutorial to help readers who need to switch versions.
I. Analysis of the Reasons to turn GPT-5 into the old GPT-4o
1. Changes in User Needs
Since the launch of GPT-5, user feedback has been distinctly polarized. On one hand, many users appreciate its more powerful generation capabilities and broader knowledge base. On the other hand, a portion of users, in practice, prefer to continue using GPT-4o. This preference is particularly evident in creative writing, technical documentation, and conversational interaction. For example, some writers and screenwriters report that GPT-4o is more stable in maintaining plot coherence and consistent language style. While GPT-5’s content is richer, it can occasionally exhibit stylistic jumps or become overly verbose.
Furthermore, different application scenarios have significantly different model requirements. For code generation and data analysis tasks, some developers find that GPT-4o’s solutions are more concise and direct. While GPT-5 can offer more diverse implementation methods, this sometimes adds unnecessary complexity to the decision-making process. This scenario-based demand has prompted users to flexibly choose the model version based on the specific task rather than blindly pursuing the “latest” one.
2. Performance and Stability
The quality of generated content is one of the main reasons many users choose to revert to GPT-4o. Although GPT-5 demonstrates a higher level of intelligence in various tests, in certain contexts, its generated content may be too verbose or deviate from the user’s expectations. For example, in technical writing that requires strict formatting, GPT-4o often provides more structured and logically clear outputs. Some users also point out that GPT-5 tends to produce more “creative” but sometimes less accurate answers, which can add an extra burden in scenarios requiring high fact-checking.
Moreover, model stability is a critical factor. Some users have reported that GPT-5’s response time can fluctuate significantly under high-concurrency or long-duration usage, whereas GPT-4o maintains more consistent performance in these situations. For enterprise users and developers, this reliability is often a key consideration in technology selection.
3. Personalization and Customization
Many users have established a “working rapport” with GPT-4o through long-term use. Whether through specific prompt structures or fine-tuned, specialized versions, users have often accumulated a wealth of usage experience and optimization strategies tailored to GPT-4o. A sudden switch to GPT-5 not only means having to re-adapt but may also render existing workflows and customized scripts ineffective.
For some niche fields (such as law, medicine, or academic research), users might also rely on domain-specific fine-tuning performed on GPT-4o. Although GPT-5 supports similar functionalities, the time and computational cost required to retrain and validate a new model make sticking with the older version a more economical choice.

4. Cost and Resources
Usage cost is a significant factor for many individual users and small teams when selecting a model. While GPT-5 is more powerful, the computational resources required for its inference are also significantly higher, which directly translates to increased API call costs and response latency. For applications that don’t require peak performance, such as routine text summarization or basic customer service bots, GPT-4o can meet the needs at a lower cost.
In addition, GPT-5 imposes higher hardware demands. Some users have observed that under identical hardware conditions, GPT-5’s throughput is noticeably lower than that of GPT-4o, particularly on systems with limited memory. This performance gap is a key reason why some resource-constrained users choose to turn GPT-5 into the old GPT-4o, preferring the older model for its greater efficiency.
II. How to turn GPT-5 into the old GPT-4o: Step-by-Step Tutorial
1. Preparation
Before starting the version conversion, make sure your system environment meets the requirements for running GPT-4o. It’s recommended to check if the AI interface platform you’re using supports model version switching and confirm that your account has the necessary permissions. Also, you should upgrade the relevant SDKs or client tools to the latest version to avoid compatibility issues.
Data backup is an indispensable step in the conversion process. If you have saved custom prompt templates, chat history, or model parameters, it’s a good idea to export and back up this data first. Most platforms support this operation through an “Export Data” function in the settings, or you can use relevant APIs for bulk backup.
2. Conversion Steps
How to Switch Back to GPT-4o
First, log in to the AI platform you’re using and navigate to the model settings interface. In an OpenAI environment, this option is usually under the “Model” or “Configuration” tab. Look for a dropdown menu named “Model Selection” or something similar and click to expand the list of available models.
If you are using the OpenAI API, you should set the model parameter in your code or API request to “gpt-4o” or a specific version number (e.g., “gpt-4o-2024-08-06”). If you are using ChatGPT Plus, you can directly select GPT-4o from the dropdown menu above the chat input box. If you are using a third-party AI platform, look for a dropdown menu in its model settings or related configuration page and make your selection there.
Next, adjust the generation parameters based on your task’s needs (primarily through the API). For tasks requiring high certainty, consider setting the Temperature to a lower value (e.g., 0.2-0.5); for creative tasks, you can raise it appropriately. Also, set the Max Tokens to a reasonable number. If you have previously optimized parameters for other models (like GPT-4-Turbo), it’s a good idea to refer to the latest documentation and re-test, as different models may respond differently to these parameters.
Once the switch is complete, be sure to perform a functionality test. Enter a series of standard test questions (like fact-checking, logical reasoning, and text generation) and compare the output with your expectations. We recommend running multiple tests before using the model for your final work to ensure it performs as required.
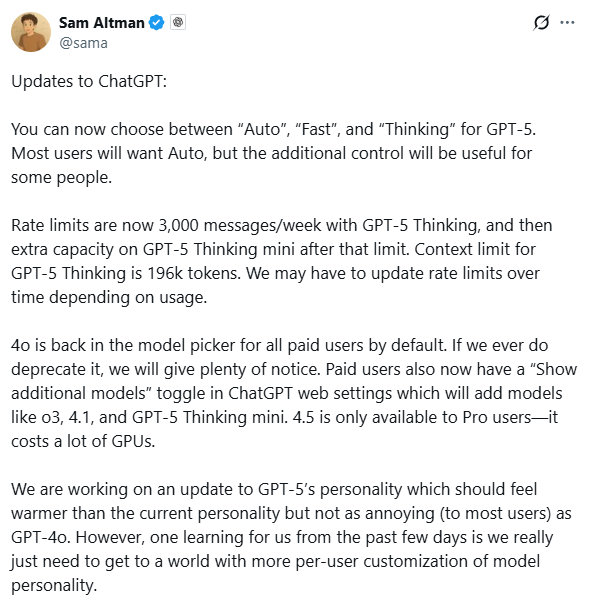
III. Common Issues When You turn GPT-5 into the old GPT-4o
During the switching process, some users may encounter situations where the model fails to load or responds abnormally. This is generally caused by an outdated cache or client compatibility issues. You can try clearing your browser cache or upgrading your SDK version before trying again.
If you notice a decline in output quality after you turn GPT-5 into the old GPT-4o, first verify that key parameter settings—such as temperature and stop sequences—are properly configured. Due to subtle differences in how GPT-4o and GPT-5 interpret instructions, it may also be necessary to recalibrate your prompts to align with the older model’s behavior.
In some cases, users who turn GPT-5 into the old GPT-4o may find that certain advanced functionalities—such as function calling or multi-modal processing—are no longer available. This is because these capabilities were introduced after GPT-4o and are not supported in the older model. If these features are essential to your workflow, you will need to carefully evaluate whether to continue using GPT-4o or return to GPT-5 until OpenAI releases possible extended updates for older versions.
IV. Summary
The decision to turn GPT-5 into the old GPT-4o is not a mere technical regression but a rational choice driven by practical user needs. Whether motivated by the demand for more stable output quality, the need to maintain personalized adaptation, or considerations regarding cost and resource efficiency, this shift reflects a broader trend in AI applications: moving from blindly pursuing the “newest” to wisely selecting the “most suitable” solution.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, users can effectively turn GPT-5 into the old GPT-4o and tailor the model to better suit their specific requirements. It’s important to remember that model selection is not a one-time decision. As AI technology continues to evolve and user needs shift, maintaining a flexible adaptation strategy remains the best practice. We also hope that future updates from OpenAI will further streamline the model upgrade process, enabling users to benefit from cutting-edge advancements while reducing the friction and cost involved when they choose to turn GPT-5 into the old GPT-4o.



