Multifactor
A password manager
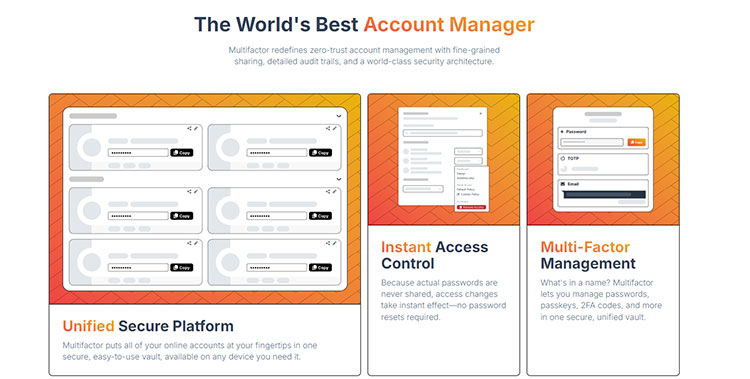
Password manager built for secure sharing with humans & AI
Website:multifactor.com
What is Multifactor?
It is an innovative password manager specifically designed for the secure sharing of accounts, supporting both human users and AI agents. Co-founded by Vivek Nair, a former CIA officer and Ph.D. in Computer Science, and Colin Roberts, a former NASA scientist and Ph.D. in Mathematics, the team boasts over a decade of cybersecurity experience, dedicated to combining cutting-edge security technology with a user-friendly experience.
The core technology of Multifactor is the “Checkpoint Link.” Users do not share passwords directly; instead, they generate a shareable link, similar to a Google Docs link, to authorize another person or an AI agent to access the account. This method not only simplifies the sharing process but also ensures immediate and controllable permission management.

Key Use Cases
It is suitable for various daily and professional scenarios, helping users manage account sharing securely and flexibly:
- Team Collaboration: For instance, an investor uses Multifactor to share email and calendar permissions with a rotating team of personal assistants, ensuring the assistants can manage the schedule without unauthorized access to critical settings.
- Professional Services: A financial advisor manages a client’s securities account via Multifactor. They can execute operations without obtaining the client’s password, which is both convenient and compliant with industry regulations.
- Lifestyle Sharing: Users share household accounts like Netflix or Instacart with roommates, with the ability to add or remove people instantly, mitigating the risk of password leaks.
These use cases highlight Multifactor’s advantage in balancing convenience and security, making it especially suitable for scenarios requiring dynamic permission management.
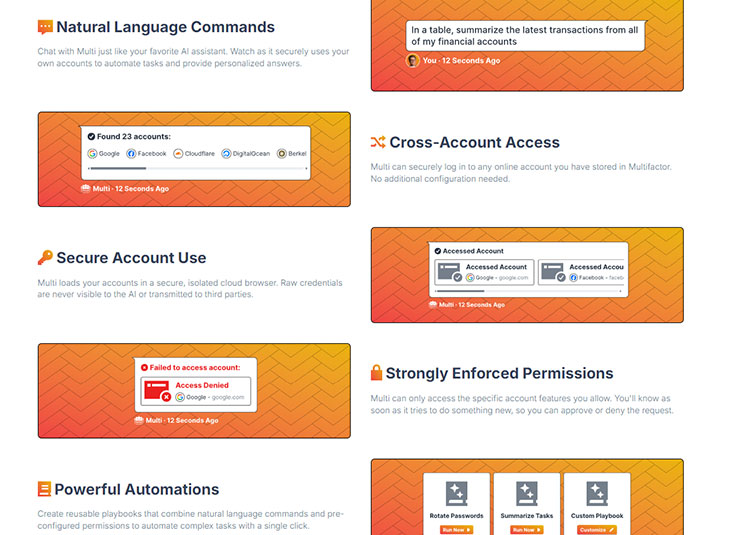
How to Integrate AI Agents?
Multifactor uses a unified Checkpoint system, allowing AI agents to securely use shared accounts just like humans. When a user sends a Checkpoint Link to an AI agent, the agent clicks the link to “log in directly” to the account without dealing with complex login procedures or storing passwords.
For example, a user can authorize an AI assistant to automatically log into an e-commerce platform to process orders or manage a social media account. The password remains completely isolated throughout the process, adhering to the OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project) recommended “Principle of Least Privilege,” which boosts automation efficiency while eliminating the risk of credential misuse.
Differences from 1Password and Dashlane
Compared to the sharing solutions offered by traditional password managers, Multifactor has three core differences:
- Fundamentally Different Sharing Mechanism: 1Password’s shared vault or Dashlane’s Teams plans are primarily based on sharing clear-text or encrypted passwords, whereas Multifactor entirely avoids password transmission. Users authorize access via a link, fundamentally lowering the risk of password leaks.
- More Granular Permission Control: Multifactor supports setting usage restrictions (e.g., view-only) and allows for instant revocation of access. In contrast, traditional password sharing requires manually changing the password to revoke access, which is cumbersome and involves a time lag.
- Future-Proofing: Multifactor offers native AI agent integration, a domain not yet covered by existing tools. According to a Gartner report, 30% of enterprises will adopt agent-based automation by 2026, and Multifactor’s architecture is better suited to this trend.
Security Architecture and Reliability
Multifactor’s security is built on three pillars:
- Zero Password Sharing: It employs tokenization technology, where all access is verified via temporary tokens, and passwords remain encrypted and stored locally on the user’s device.
- Instant Permission Revocation: Revoking a link immediately terminates access; even if the recipient is logged in, they are forcibly logged out, preventing the risk of “stale background logins” common with traditional password sharing.
- End-to-End Encryption: Data encryption adheres to the AES-256 standard, consistent with bank-grade protection, ensuring security throughout transmission and storage.
Future Development Plan
Multifactor’s roadmap focuses on intelligence and openness:
- Multi AI Assistant: The imminent launch of an AI assistant specializing in secure account usage, capable of automating tasks like logging in and data querying.
- Developer API: Future plans to open an API, allowing enterprises to integrate Multifactor into internal systems or third-party applications.
- Enterprise Plan: Introduction of an advanced features enterprise solution, including audit logs and SAML integration, alongside the perpetual free version.
Target User Groups
Multifactor is particularly suitable for the following groups:
- Team Managers: Businesses or project groups that require dynamic allocation of account permissions.
- Professionals: Roles such as lawyers and consultants who need to act on behalf of clients’ accounts while adhering to confidentiality agreements.
- Technical Developers: Individuals or enterprises looking to integrate AI agents for automation tasks.
- Family and Shared-Life Users: General consumers managing shared accounts for streaming, e-commerce, and other services.
By transforming password sharing into link authorization, Multifactor reshapes collaboration efficiency while enhancing security. As cybersecurity expert Bruce Schneier states: “True security is not about increasing barriers, but about intelligently managing access.” Multifactor is using this philosophy to drive account sharing into a new era.